Abstract
Motivation: RNA-seq has been extensively used for transcriptome study. Quality control (QC) is critical to ensure that RNA-seq data are of high quality and suitable for subsequent analyses. However, QC is a time-consuming and complex task, due to the massive size and versatile nature of RNA-seq data. Therefore, a convenient and comprehensive QC tool to assess RNA-seq quality is sorely needed.
Results: We developed the RSeQC package to comprehensively evaluate different aspects of RNA-seq experiments, such as sequence quality, GC bias, polymerase chain reaction bias, nucleotide composition bias, sequencing depth, strand specificity, coverage uniformity and read distribution over the genome structure. RSeQC takes both SAM and BAM files as input, which can be produced by most RNA-seq mapping tools as well as BED files, which are widely used for gene models. Most modules in RSeQC take advantage of R scripts for visualization, and they are notably efficient in dealing with large BAM/SAM files containing hundreds of millions of alignments.
Availability and implementation: RSeQC is written in Python and C. Source code and a comprehensive user’s manual are freely available at:http://code.google.com/p/rseqc/.
Contact: WL1@bcm.edu
Introduction
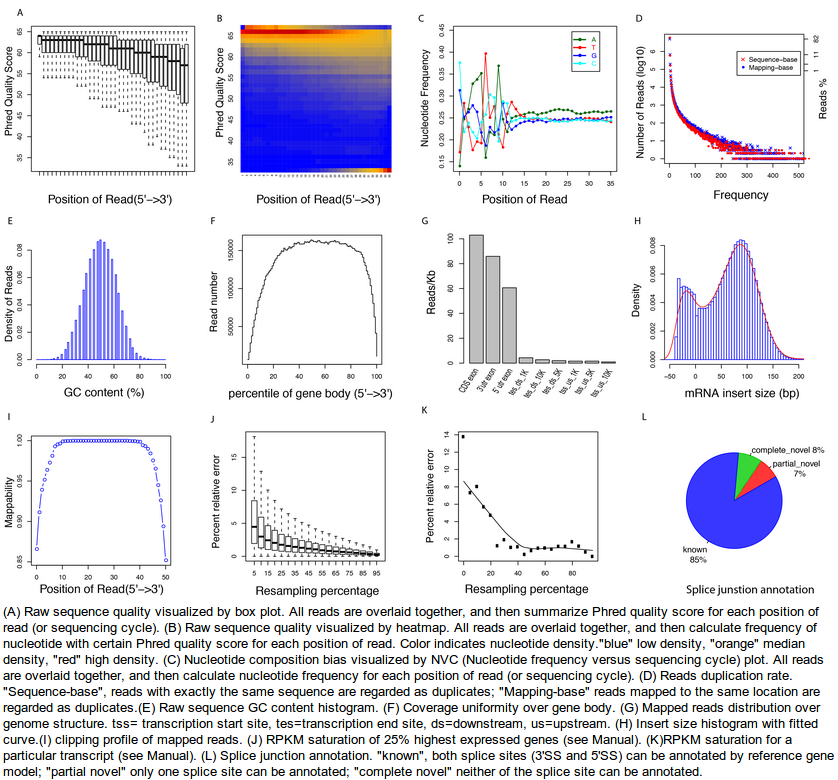
RSeQC package provides a number of useful modules that can comprehensively evaluate high throughput sequence data especially RNA-seq data. “Basic modules” quickly inspect sequence quality, nucleotide composition bias, PCR bias and GC bias, while “RNA-seq specific modules” investigate sequencing saturation status of both splicing junction detection and expression estimation, mapped reads clipping profile, mapped reads distribution, coverage uniformity over gene body, reproducibility, strand specificity and splice junction annotation
RSeQC Manual
Download RSeQC from BCM or go to Downloads page
Release history
RSeQC v2.3.1:
- Add normalization option to bam2wig.py. With this option, user can normalize different sequencing depth into the same scale when converting BAM into wiggle format.
- Add another script. geneBody_coverage2.py. This script uses BigWig instead of BAM as input, and requires much less memory (~ 200M)

Recent Comments