install.packages("BiodiversityR")
library(BiodiversityR)
library(vegan)
data(dune.env)
data(dune)
RankAbun.1 <- rankabundance(dune)
RankAbun.1
rankabunplot(RankAbun.1,scale='abundance', addit=FALSE, specnames=c(1,2,3))
rankabuncomp(dune, y=dune.env, factor='Management',
scale='proportion', legend=FALSE)
mcranndata<-read.csv(file="mcra.nn.shared.csv", header=T, sep="\t")
row.names(mcranndata)<-mcranndata$Group;
mcranndata_matrix<mcranndata[,3:623]
rankabuncomp(mcranndata_matrix, y=reladata, factor='Group', scale='logabun',scaledx=T, type='l', xlim=c(5,200))
Functions ‘rankabundance’ and ‘rankabuncomp’ allow to calculate
rank abundance curves for subsets of the community and
environmental data sets. Function ‘rankabundance’ calculates the
rank abundance curve for the specified level of a selected
environmental variable. Method ‘rankabuncomp’ calculates the rank
abundance curve for all levels of a selected environmental
variable separatedly.
scaledx: Scale the horizontal axis to 100 percent of total number of
species.
scale: Method of scaling the vertical axis. Method "abundance" uses
abundance, "proportion" uses proportional abundance (species
abundance / total abundance), "logabun" calculates the
logarithm of abundance using base 10 and "accumfreq"
accumulates the proportional abundance.
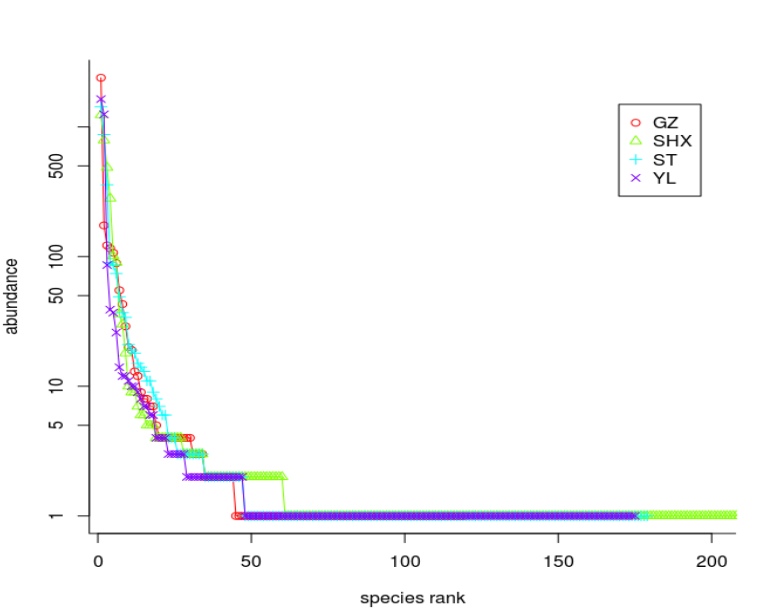
mcra.nn.shared


Recent Comments